Revolutionizing Healthcare with Spatial Computing: AR in Surgeries and Training
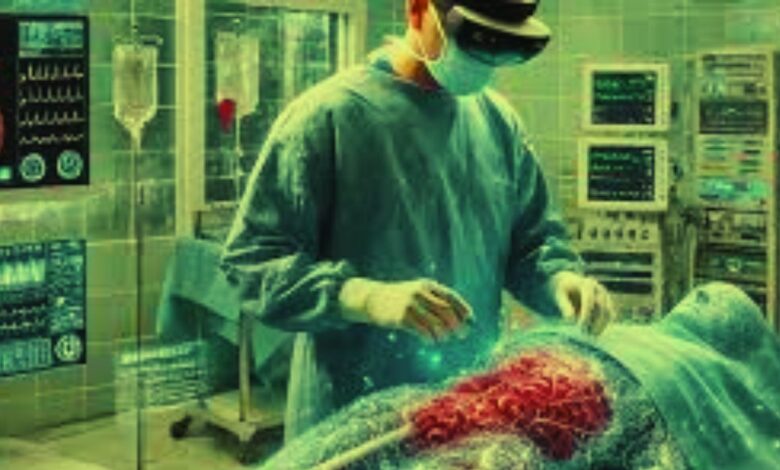
In recent years, the integration of spatial computing, particularly Augmented Reality (AR), has begun to transform healthcare in profound ways. By merging the physical and digital worlds, AR technology has opened new possibilities for improving surgical procedures and training programs. This article delves into how AR is revolutionizing surgeries and medical education, paving the way for a future where healthcare is more precise, accessible, and effective.
The Role of Augmented Reality in Surgeries
Augmented Reality (AR) enables surgeons to overlay digital information directly onto the patient’s body during a procedure. This technology enhances real-time decision-making by providing vital data, such as 3D images of organs, tissues, and blood vessels, without requiring separate screens or instruments. Surgeons can now visualize structures beneath the surface, often invisible to the naked eye, and make more informed choices in the operating room.
One of the most remarkable benefits of AR in surgery is its ability to reduce the risk of human error. For example, in complex procedures like brain surgery, AR can display 3D images of the patient’s brain, highlighting critical areas that require attention. This level of visualization significantly minimizes the chance of accidentally damaging surrounding healthy tissues.
Moreover, AR aids in minimally invasive surgeries by guiding the surgeon’s movements with precision. Using AR, surgeons can perform procedures through smaller incisions, leading to shorter recovery times, less trauma to the body, and reduced risk of infection.
Enhanced Precision and Accuracy in Surgical Procedures
AR in surgeries provides an enhanced level of precision that was previously unimaginable. In traditional surgeries, there are many unknowns about the patient’s internal anatomy. With AR, surgeons can see exactly where they need to cut, avoiding unnecessary incisions. This leads to better patient outcomes, shorter recovery periods, and a lower risk of complications.
Take, for instance, the use of AR in orthopedic surgery. By visualizing the bones and surrounding tissues in 3D, orthopedic surgeons can place implants or repair fractures with much greater accuracy. This kind of precision is invaluable in highly intricate surgeries like spinal or joint procedures, where any error can lead to long-term consequences.
AR’s Role in Training the Next Generation of Surgeons
Apart from its role in active surgeries, AR is revolutionizing the way future healthcare professionals are trained. Medical students and resident surgeons can use AR simulations to practice various surgical procedures in a risk-free, controlled environment. These simulations provide an immersive learning experience that traditional textbooks and video tutorials cannot match.
AR allows students to interact with 3D models of human anatomy and perform mock surgeries on them. For example, they can practice delicate procedures such as suturing or tissue dissection without the need for live patients or cadavers. Additionally, AR enables the visualization of complex procedures step by step, allowing students to understand the anatomy and techniques involved in detail before attempting them in real-life scenarios.
Furthermore, AR-based training platforms can be personalized to the learner’s skill level, offering real-time feedback and guidance. This tailored approach accelerates the learning curve and builds confidence among trainees.
Collaboration and Remote Assistance in Healthcare
AR is also transforming the way healthcare professionals collaborate. With AR glasses and other wearable devices, surgeons and specialists can share their viewpoint with colleagues in real time, regardless of their physical location. This makes remote consultations more interactive and effective, enabling expert guidance from afar.
For instance, in a scenario where a surgeon is performing a complex procedure, an experienced doctor from across the globe can virtually “see” the surgery in real time through the AR system. They can provide advice, suggest alternatives, or guide the surgeon step by step, offering invaluable support in high-pressure situations.
This ability to collaborate remotely has also expanded the reach of high-quality healthcare to underserved or remote regions, where access to specialized care may be limited.
Challenges and Future Potential
Despite its promising benefits, the adoption of AR in healthcare does face some challenges. The high cost of AR technology and the need for specialized hardware can be barriers for many healthcare providers, especially those in resource-limited settings. Additionally, integrating AR into existing surgical and medical systems requires significant training and infrastructure development, which can be time-consuming and costly.
However, as technology evolves and becomes more affordable, AR is expected to become a staple in healthcare worldwide. Its ability to improve outcomes, enhance training, and support collaboration will continue to drive innovation and make healthcare more efficient and accessible.
Conclusion
Augmented Reality is proving to be a game-changer in healthcare, particularly in surgeries and medical training. By offering enhanced precision, real-time visualization, and immersive learning experiences, AR is empowering healthcare professionals to perform better, safer procedures. As the technology becomes more accessible and refined, its potential to revolutionize the field of medicine will only grow, leading to better patient outcomes, advanced medical education, and more collaborative care. With AR, the future of healthcare is not just a distant vision—it’s happening now.